📘 Embeddings
Vector
A vector is an array of numbers that represent magnitude and direction in a multi-dimensional space.
Embeddings
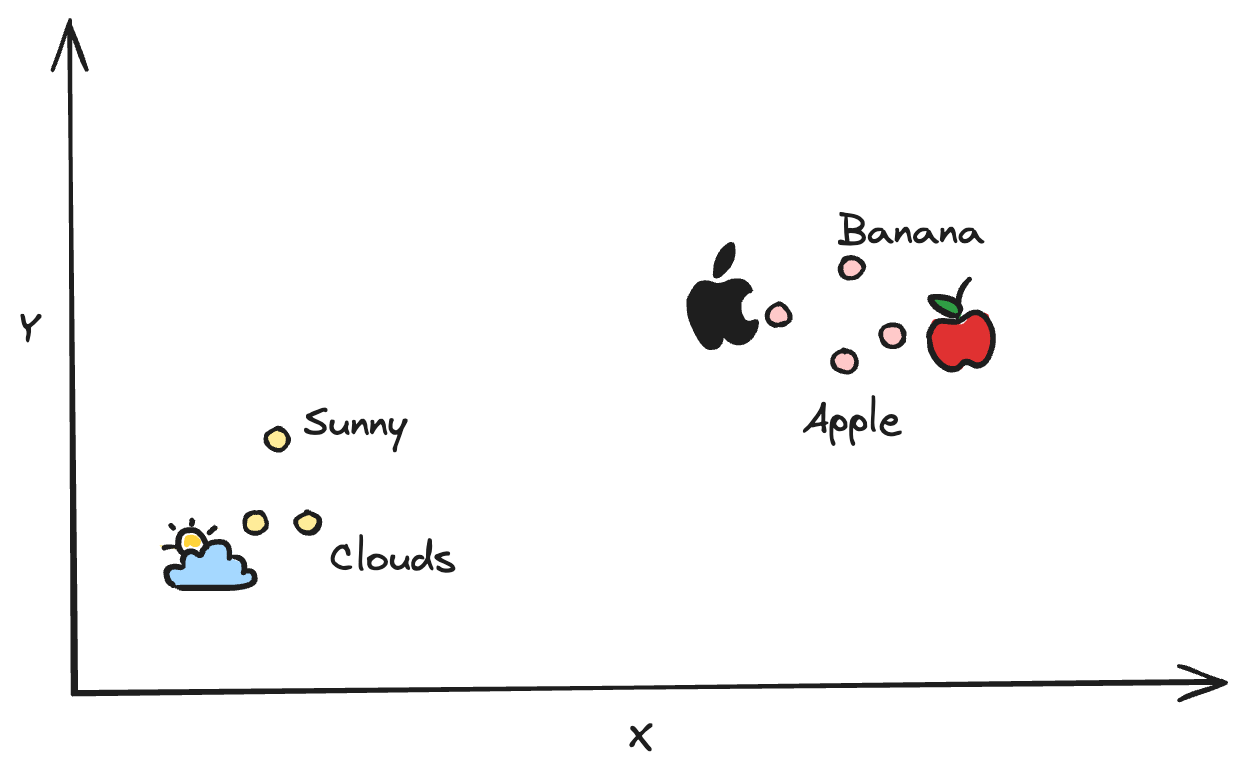
Embeddings are vectors that represent a piece of information, such as text, images, audio, video etc. Embeddings capture semantic qualities of the data i.e. characteristics that capture the meaning or essence of it.
This way, if you plot data in this multi-dimensional vector space, semantically similar data, or data with similar meaning ends up close to each other.
Embedding models
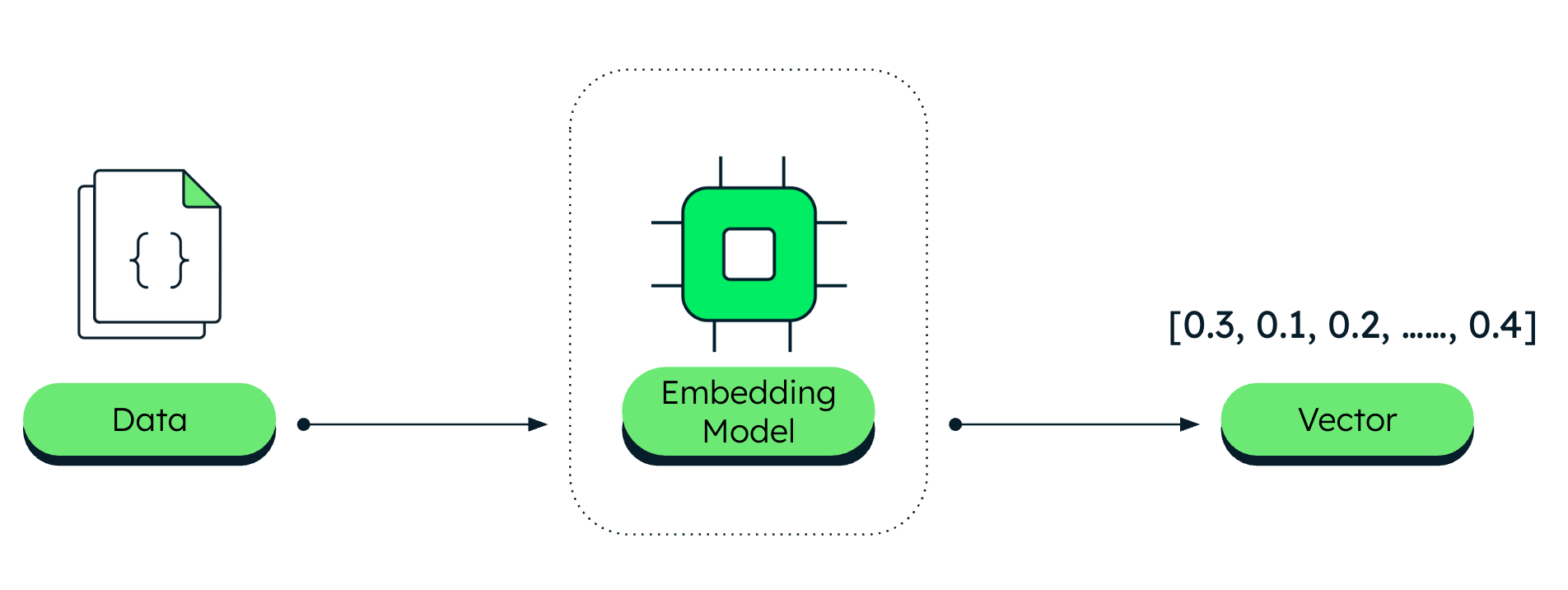
Embedding models are specialized machine learning models that have been trained to convert a piece of information to these numerical encodings.
The embedding model you choose determines the number of elements in the embedding vectors, and consequently the number of dimensions required to represent them in vector space.
Embedding models vary depending on how the model was trained. Therefore, different models offer different advantages depending on your data and use case. While text embedding models are widely used, embedding models also exist for other types of data such as images, audio, and multimodal content.