📘 Atlas Search architecture
Atlas Search provides powerful findability capabilities to your data collections. A flexible index configuration allows mapping and indexing only the fields needed, or dynamically mapping any and all fields supported.
The Big Picture
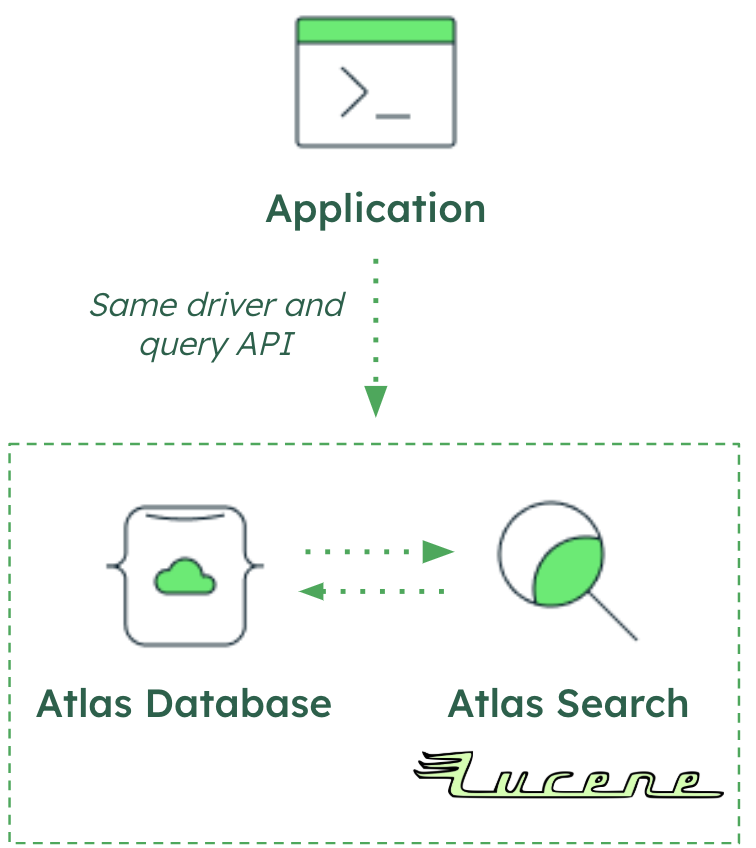
Applications communicate to Atlas Search through the same mechanism as all other requests: an aggregation pipeline through a MongoDB driver.
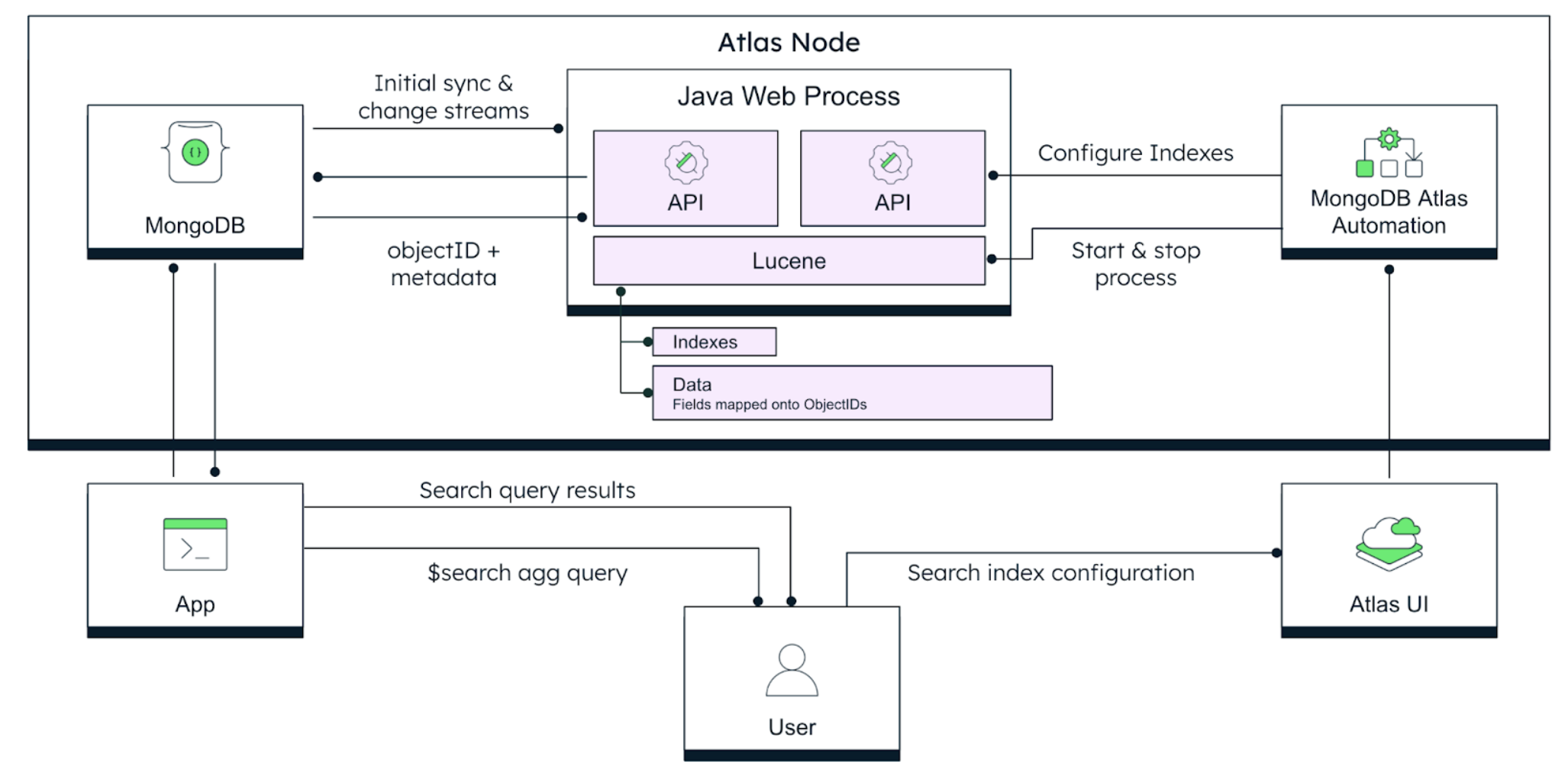
System architecture
The Atlas Search mongot process, built on Apache Lucene, interfaces with the mongod
database process to create and manage full-text (and vector search) indexes and queries.
The mongot process performs the following tasks:
- Creates Atlas Search indexes based on the index definition.
- Monitors change streams for the current state of the documents.
- Processes Atlas Search queries and returns the document IDs and other search metadata for
the matching documents to
mongod, which then does a full document lookup and returns the results to the client.
Changes to a collection via updates, deletes, or additions are eventually consistent, meaning the index is updated independently of changes to the collection in a separate process, asynchronously. The lag between a change made to the database and refelected in a subsequent search is dependent on many factors such as deployment tier and architecture, the complexity of the index mapping, the other changes that are also queued, and the laws of physics.
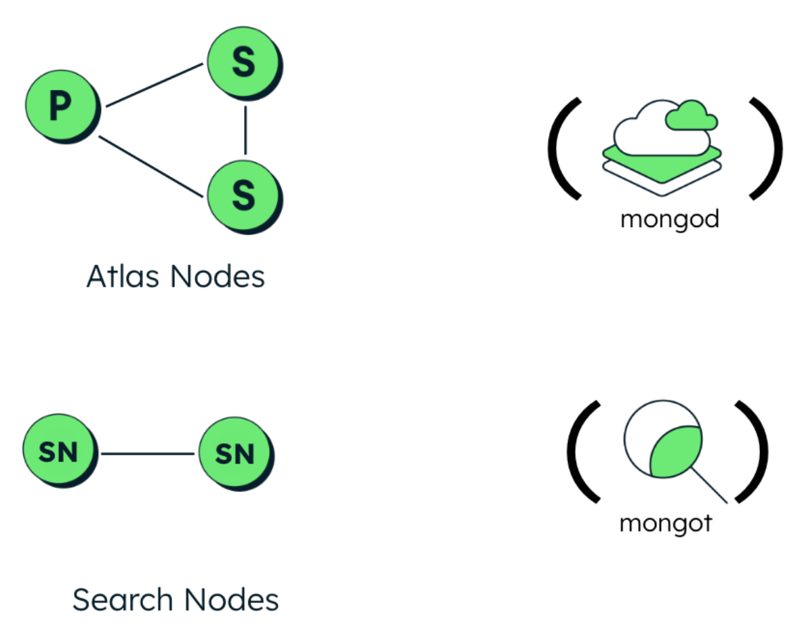
The Atlas Search process can be deployed either coupled alongside the database nodes, or on separate dedicated nodes. Dedicated nodes provide separation of concerns, alleviating resource contention. Dedicated search nodes are recommended for production workloads.
Coupled nodes
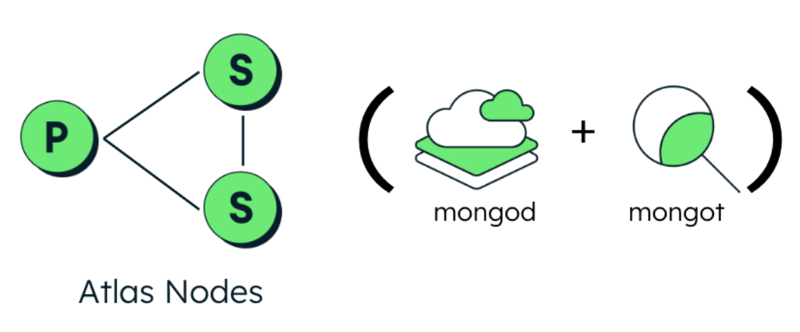
Dedicated search nodes