👐 Setup
GitHub Codespaces
You will be working in GitHub Codespaces throughout this lab. A codespace is a cloud-hosted, containerized development environment that comes pre-configured with all the tools you need to run this lab.
Navigate to this link. You will be prompted to sign into GitHub if you haven't already. Once signed in, click the Create new codespace button to create a new codespace.
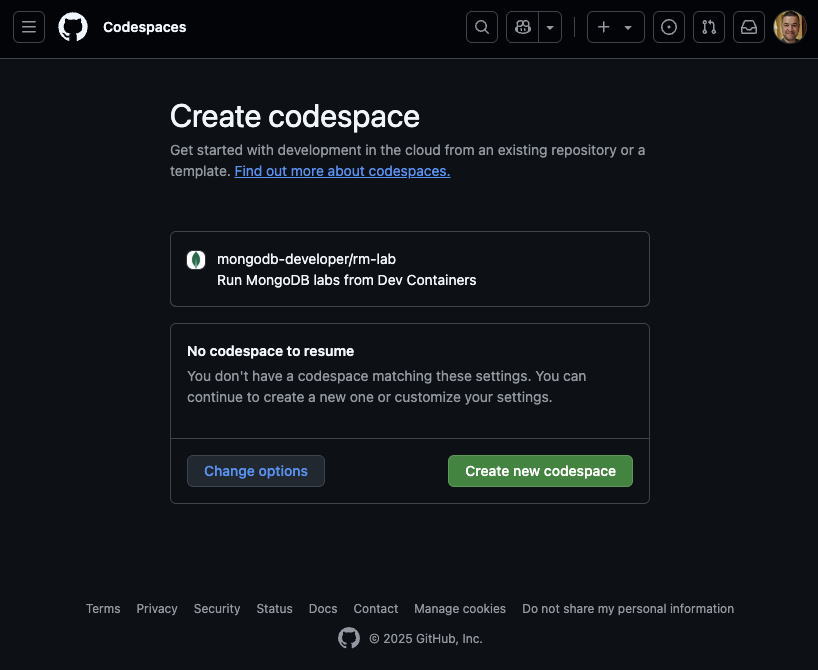
Let it run for a few minutes as it prepares a Docker container with all the required libraries and a MongoDB cluster.
That's it! You're ready for the lab!
During the lab, we will use GitHub Codespaces. The following instructions are here just in case you can't use Codespaces or if you really, really, really want a local installation.
🦹 Run this lab locally
Again: during the lab, we will use GitHub Codespaces. The following instructions are here just in case you can't use Codespaces or if you really, really, really want to try a local installation.
1. MongoDB Database
As we'll be importing data from a Relational Database into MongoDB, you'll need to have a MongoDB database. You have a few options to set up this database.
🦸 Option A: New MongoDB Atlas cluster
The easiest way to run MongoDB is to use MongoDB Atlas, our cloud-hosted database offering. You can set a MongoDB Atlas account and a free forever M0 Cluster.
To get yours, follow the instructions on the Intro Lab:
Be sure to open up the cluster to allow connections from your local computer, and configure a database user with the readWriteAnyDatabase role.
🦸 Option B: Use an existing cluster
If you have an existing MongoDB Atlas, Enterprise or Community cluster, you can use it as the migration target. Make sure you know the URI for the cluster, and have a database user with the readWriteAnyDatabase role.
🦸 Option C: Run a MongoDB container using Docker
If you don't have an existing MongoDB server but have Docker installed, you can easily load a container pre-configured with MongoDB by running the following command:
docker run -p 27017:27017 mongo
This will launch an empty MongoDB community cluster on localhost:27017, suitable to use for this lab. You can connect with no username or password. Since this command does not use Docker volumes, any data will be lost when the container is stopped.
2. MongoDB Relational Migrator
Download and install MongoDB Relational Migrator.
- Open the MongoDB Relational Migrator downloads page
- Select your platform (OS / Architecture if applies) and download it.
- Install the MongoDB Relational Migrator.
- Launch it.
- It should open a browser at the address http://127.0.0.1:8278/
- You should see an icon to launch/quit the Relational Migrator.
There are other, more advanced ways to install the MongoDB Relational Migrator. You can check them out in the installation docs page. These won't be covered during this Lab.