👐 Build a compound index following the ESR rule
In this exercise, you will build a compound index following the ESR rule, compare the query explain plans before and after creating the index, and analyze them.
Explore the code
- 🚀 NodeJS/Express
- ☕️ Java Spring Boot
-
Open the file
server/src/indexing/borrowed-books-index.tsfile in your GitHub Codespace. -
Examine the code to build a compound index on the
issueDetailscollection./**
* Create the index to support the following query:
* issueDetails.find({
* 'user._id': userID,
* borrowDate: { $gte: date },
* }, {
* sort: { returnedDate: -1 }
* })
*/
await collections?.issueDetails?.createIndex({
// Equality
'user._id': 1,
// Sort
returnedDate: 1,
// Range
borrowDate: 1,
});infoThe index is created on the
issueDetailscollection to support the query that finds the issue details for a user with a specificuserID, where theborrowDateis greater than or equal to a specificdate, and sorts the results byreturnedDatein descending order.This is compound index and it follows the ESR rule: Equality, Sort, and Range. This ensures optimal performance for the query.
-
Execute the script to create the compound index.
npx tsx src/indexing/borrowed-books-index.tsAfter a few seconds, you should see the following output:
Connecting to MongoDB Atlas...
Connected!
BEFORE creating the index
Winning plan stage: COLLSCAN
No index used
Total documents examined: 1284
Number of documents returned: 3
-----------------------------
AFTER creating the index
Winning plan stage: IXSCAN
Index used: user._id_1_returnedDate_1_borrowDate_1
Total documents examined: 3
Number of documents returned: 3infoThe script uses explain plans to compare the query plans before and after creating the index.
Notice the difference in the winning plan stage and the number of documents examined before and after creating the index.
-
Let’s start with our
IssueDetailrecord. Right now, it looks like this:src/main/java/com/mongodb/devrel/library/domain/model/IssueDetail.java@Document(collection = "issueDetails")
public record IssueDetail(
// fields ..
) {} -
Now let’s optimize queries that need to filter or sort by multiple fields. For example, we often query by
user._id,returnedDate, andborrowDatetogether. To speed this up, we can add a compound index using the @CompoundIndex annotation.src/main/java/com/mongodb/devrel/library/domain/model/IssueDetail.java@Document(collection = "issueDetails")
@CompoundIndex(
name = "user_returned_borrow_idx",
def = "{'user._id': 1, 'returnedDate': 1, 'borrowDate': 1}")
public record IssueDetail(
// fields
){}infoThe index is created on the
issueDetailscollection to support the query that finds the issue details for a user with a specificuserID, where theborrowDateis greater than or equal to a specificdate, and sorts the results byreturnedDatein descending order.This is compound index and it follows the ESR rule: Equality, Sort, and Range. This ensures optimal performance for the query.
-
Open the
application.ymland include the propertyauto-index-creation: true. At the end, your configuration will look like this:src/main/resources/application.ymlspring:
data:
mongodb:
uri: ${MONGODB_URI}
database: library
auto-index-creation: true
This ensures that any indexes defined in your domain models (for example, with @Indexed) will be created automatically by Spring Data MongoDB at startup.
-
Stop the running app.
- Locate the bottom panel and click on the
TERMINALtab. - Press Ctrl+C/Cmd+c to interrupt the running app
- Locate the bottom panel and click on the
-
Restart the app typing in the Terminal:
mvn spring-boot:run
As soon as the application starts, you will see log entries showing the creation of indexes, similar to the image below.
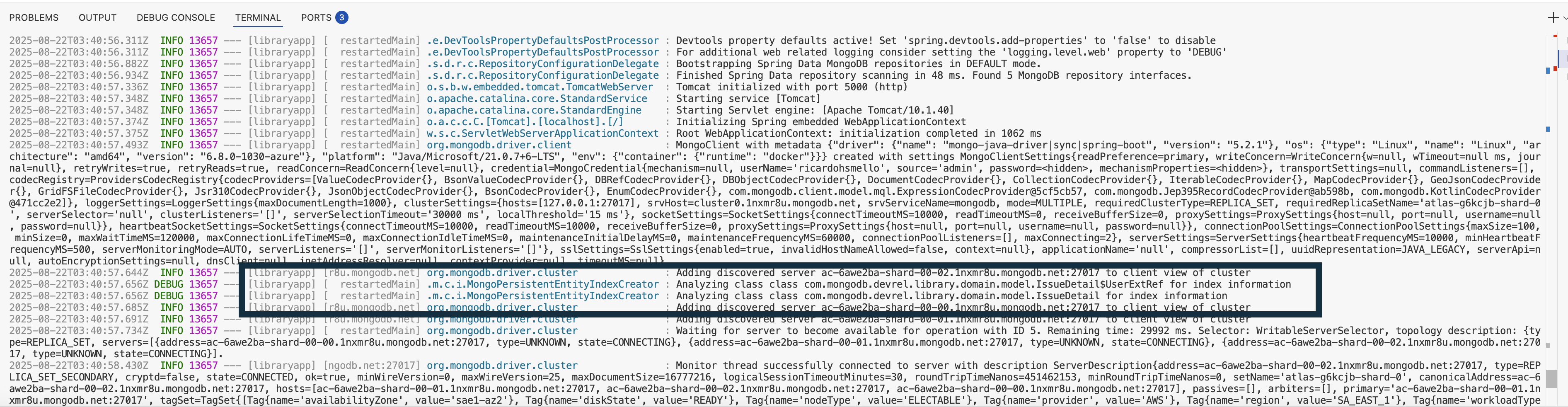
Verify that the index is created
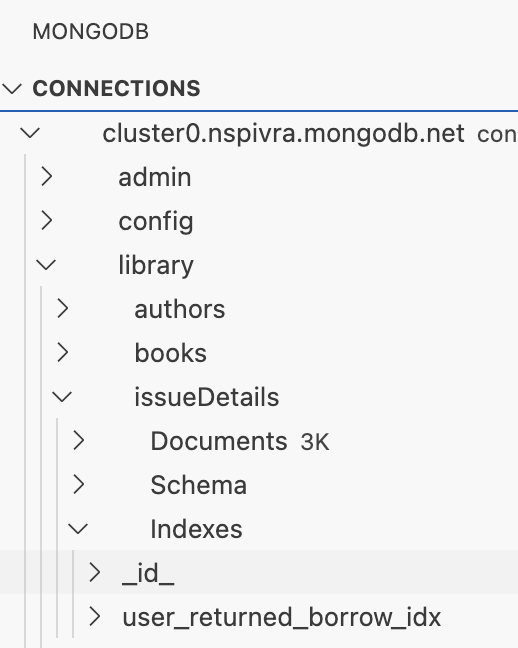
- Open the MongoDB extension (leaf icon) from the sidebar on the left.
- Click on Library DB to connect to the local MongoDB Atlas deployment.
- Expand the library database, then the issueDetails collection, and finally select Indexes.
🦸♀️ Try different indexes
Modify the compound index by adding and removing fields, and observe the changes in the query explain plans.